Charging your electric vehicle
Electric vehicle (EV) charging is commonly categorized into different levels based on the charging power and speed. Here's an overview of the three main levels of electric vehicle (EV) charging: Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3.
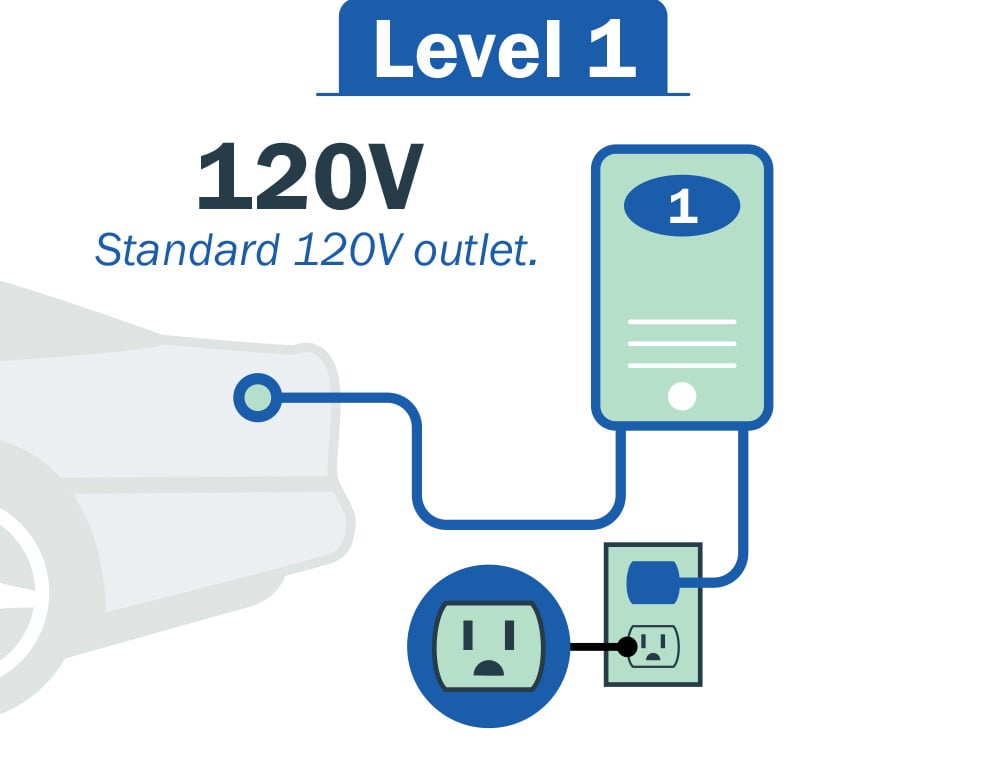
Level 1 - Charging
The basic charging method that uses a standard household outlet, typically 120-Volts. This type of charging is the slowest and provides the lowest power output. Level 1 charging cables usually come with electric vehicles and can be plugged directly into a standard wall socket. However, it is important to note that Level 1 charging is typically not suitable for daily charging needs, as it takes a longer time to fully recharge the EV battery. It is primarily used when one of the charging options below are not available.
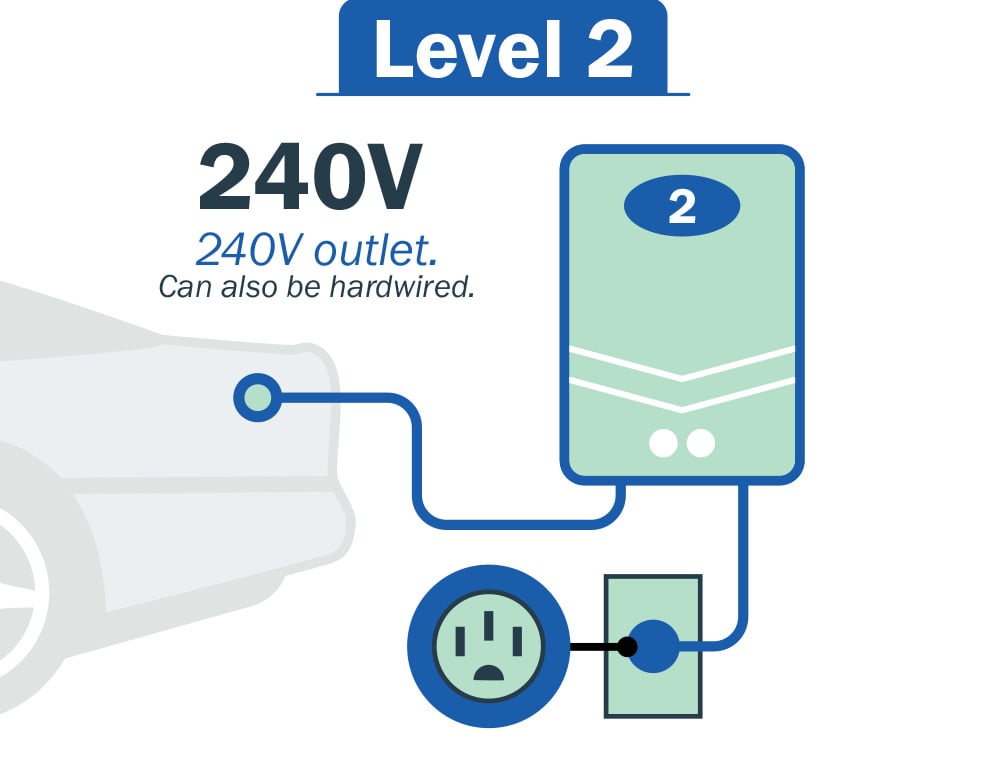
Level 2 - Charging
Faster and more advanced than Level 1. It requires the installation of a dedicated charging station and is suitable for home, workplace and public charging. Level 2 charging uses a 240-Volt Alternating Current (AC) power source, similar to a typical dryer or stove outlet. The charging power provided is significantly higher than Level 1, enabling quicker charging times. Level 2 charging can fully charge an electric vehicle in a few hours, depending on the vehicle's battery capacity. It is the most common type of charging.
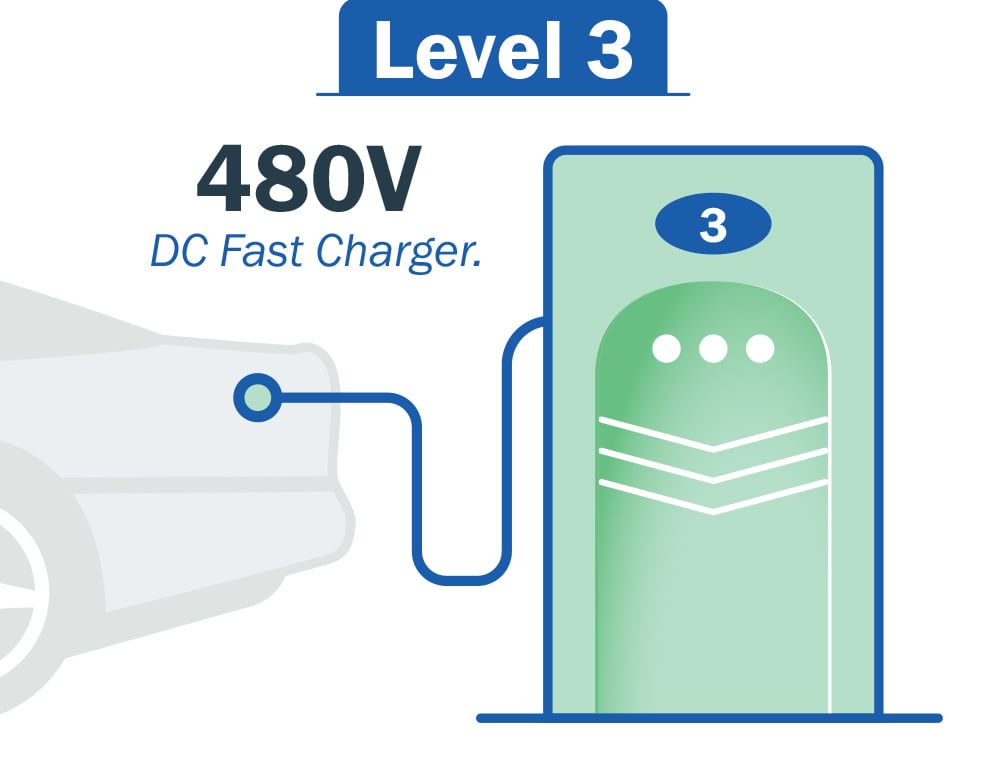
Level 3 - Charging
Also known as Direct Current Fast Charging (DCFC), is the fastest charging option available for electric vehicles. It utilizes high-power Direct Current (DC) charging infrastructure to rapidly charge the EV battery. DCFC stations can provide charging powers of several hundred kilowatts, significantly reducing charging times. These charging stations are typically found in public locations such as along highways, at service stations, and even some rest stops. DCFC can charge an electric vehicle to 80 percent or more in approximately 30 minutes, making it suitable for long-distance travel.
It's important to note that the availability and performance of DCFC stations may vary depending on the region and the specific electric vehicle model, as not all EVs are equipped to accept Level 3 charging.
Various connectors you may encounter
The J-1772, CCS, Tesla NACS and CHAdeMO connectors are commonly used in electric vehicle charging infrastructure in the United States. Each connector serves a different purpose and is associated with specific EV models or charging standards. Here's a brief overview of each connector:

J-1772 (SAE J1772)
The J-1772 connector, developed by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), is a standard connector used by many electric vehicles, especially in North America and Japan. It features a standard 5-pin design and is widely supported by various EV charging stations and manufacturers. The J-1772 connector provides Level 1 and Level 2 charging, offering moderate charging speeds.

CCS (Combined Charging System)
The CCS connector, also known as Combo connector, is a fast-charging standard that combines the existing J-1772 connector for AC charging with additional DC fast-charging capabilities. It features an extra set of pins for high-power DC charging. Although CCS is popular worldwide and is commonly used by major EV manufacturers in Europe and North America today, most EV manufacturers have made announcements to adopt Tesla’s NACS connector (see below).

Tesla NACS (Tesla Connector)
The Tesla NACS, also known as the Tesla Connector, is a proprietary charging connector designed by Tesla for their electric vehicles. It is primarily used in Tesla Supercharger stations. Tesla vehicles come with a built-in adapter that allows them to connect to other charging standards. In 2023, most EV manufacturers announced they will switch to NACS, including Ford, General Motors, Toyota and Hyundai Motor Group – the four highest-volume automakers in the U.S. Most of these non-Tesla manufacturers will offer standard NACS ports in 2026.

CHAdeMO
CHAdeMO is a fast-charging connector developed by the CHAdeMO Association, primarily used by Japanese automakers. It stands for "CHArge de MOve" and is designed to deliver high-power DC charging. While CHAdeMO was widely adopted in the past, it is gradually being phased out.
It's important to note that some EVs, particularly those from Tesla, are equipped with adapters that allow them to connect to different types of charging connectors, expanding compatibility options for charging. Additionally, the availability of these connectors may vary depending on the region and the specific charging infrastructure in place.
The best way to charge your EV at home
Watch this video to learn more about what type of charger may be right for you.
